
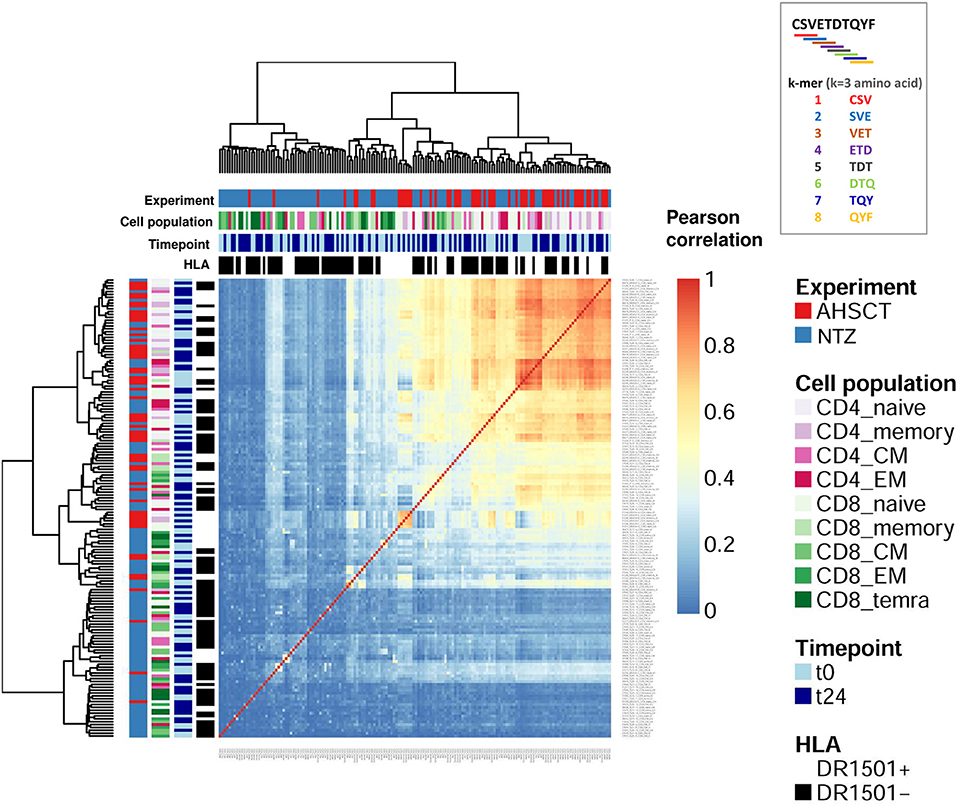
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is considered a T cell–mediated inflammatory demyelinating disorder of the central nervous system (CNS reference 1), although other immune factors such as complement and antibodies as well as factors intrinsic to the CNS are thought to contribute to disease expression. These data are the first to demonstrate that long-term suppression of inflammatory activity in MS patients who received HSCT does not depend on persisting lymphopenia and is associated with profound qualitative immunological changes that demonstrate a de novo regeneration of the T cell compartment. Analysis of the T cell receptor repertoire showed the reconstitution of an overall broader clonal diversity and an extensive renewal of clonal specificities compared with pretherapy. Phenotypic and T cell receptor excision circle (TREC) analysis confirmed a recent thymic origin of the expanded naive T cell subset. After numeric recovery of leukocytes, at 2-yr follow-up there was on average a doubling of the frequency of naive CD4 + T cells at the expense of memory T cells. To understand whether the beneficial effects on the course of disease are mediated by lympho-depletive effects alone or are sustained by a regeneration of the immune repertoire, we examined the long-term immune reconstitution in patients with MS who received HSCT. Clinical trials have indicated that autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) can persistently suppress inflammatory disease activity in a subset of patients with severe multiple sclerosis (MS), but the mechanism has remained unclear.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
